fungi life cycle explained
The process of sexual reproduction. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an.
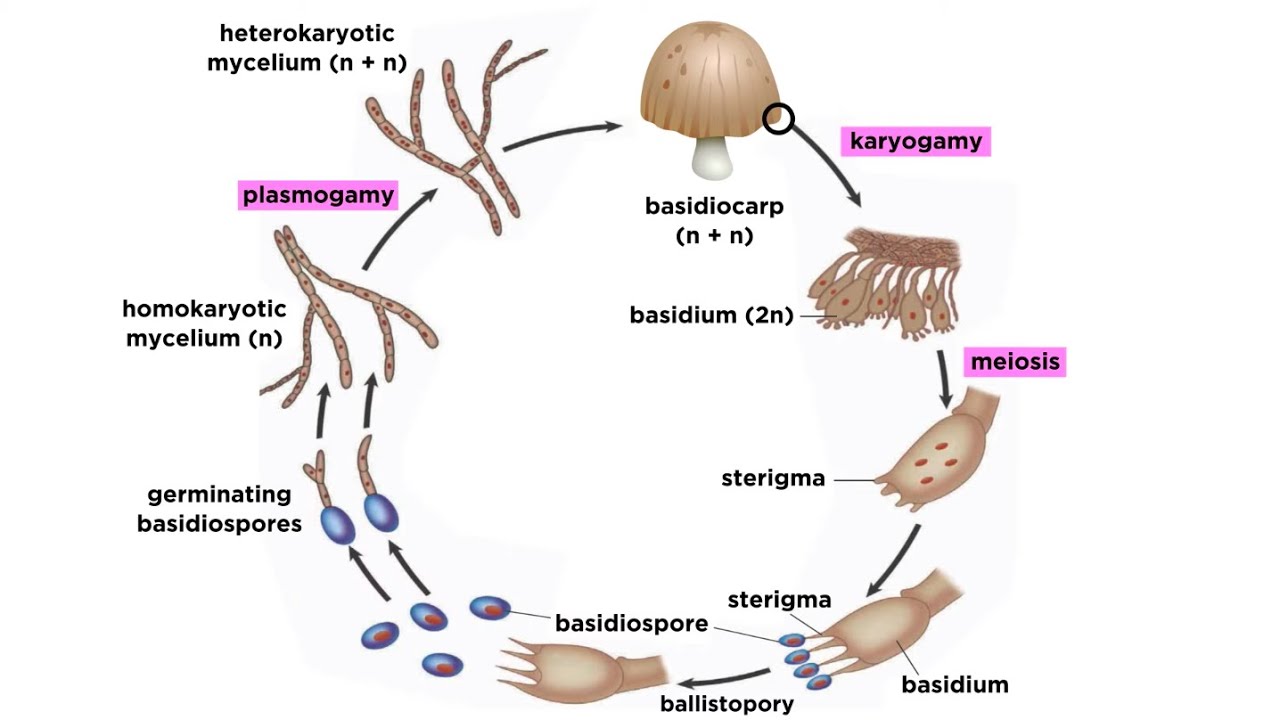
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube
Some fungi alternate between single-celled yeast and multicellular forms.

. Despite their diversity in many features the Ascomycetes. Life Cycle of Fungi. Sexual reproduction is carried out by diffusion of compatable nuclei from two parent at a definite state in the life cycle of fungi.
While some fungi reproduce sexually others. This is when mycelium comes together to form a knot near the surface of the soil which. During the anamorphic stage the fungus is able to reproduce asexually.
Spore germ hypha mature mycelium. The first sign of an emerging mushroom is a hyphal knot. Identify and describe the key adaptations unique to fungi cell walls made of chitin and external digestion including morphological life cycle and metabolic traits.
In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of ascomycetes explained with the help of a suitable diagram. Have aquatic spores that infect amphibians. Sexual reproduction in fungi.
Some fungi are multicellular while others such as yeasts are unicellular. There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. An Overview The fungi kingdom is an essential part of the Earths ecosystem and integral for its health and survival.
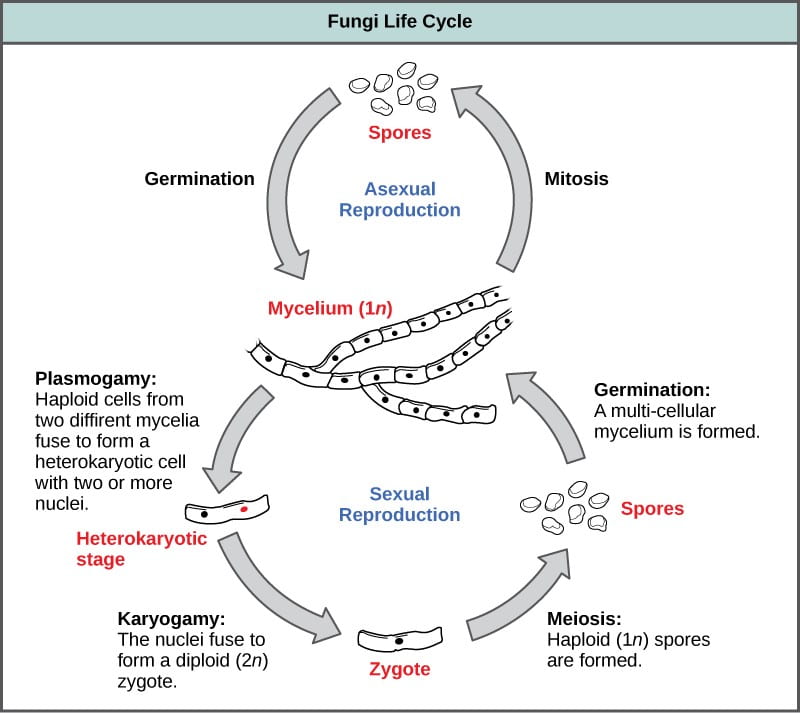
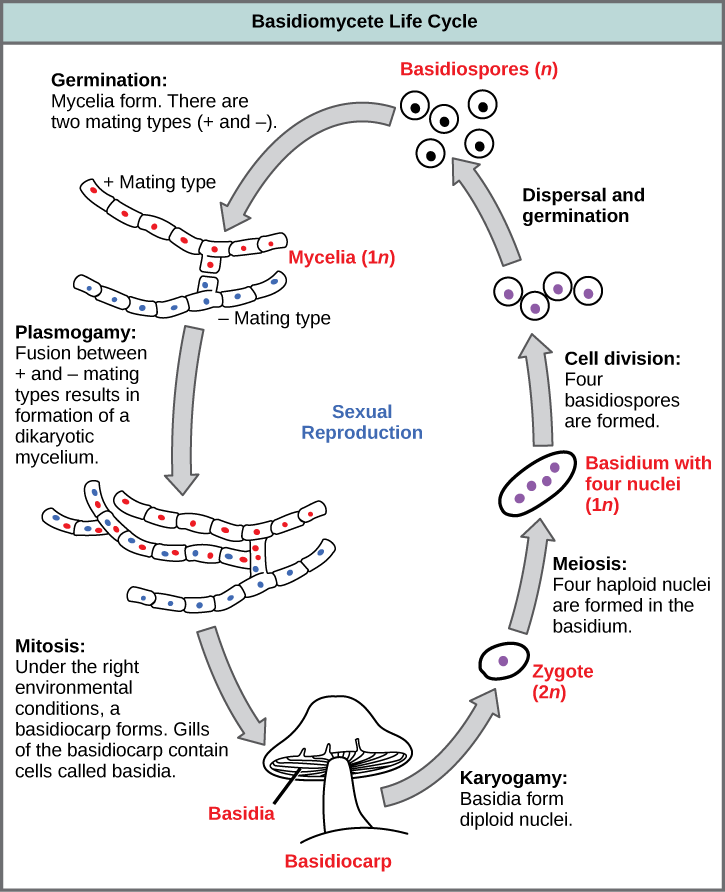
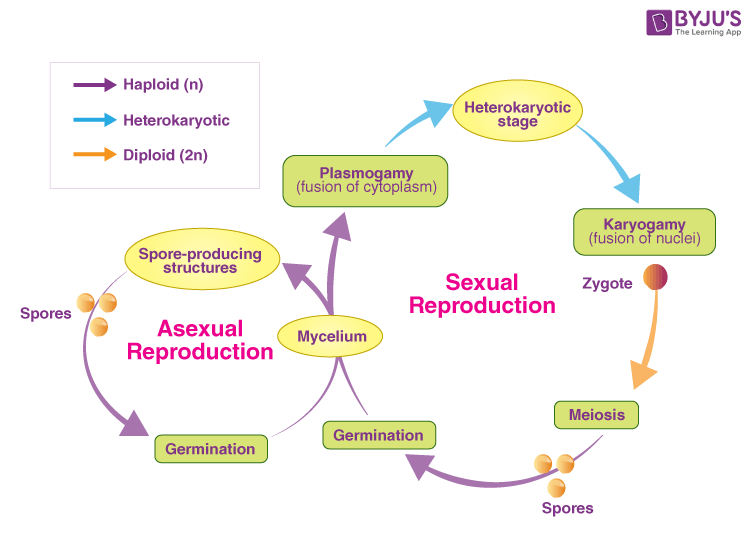
When hyphae from 2 genetically different haploid mycelia meet release pheromones. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins.
See examples of fungi that are Basidiomycetes. The Life Cycle of Fungi. For most of the molds indoors fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle.
Fungal life cycles spores and more. Fungus plural fungi any of about 144000 known species of organisms of the kingdom Fungi which includes the yeasts rusts smuts mildews molds and mushrooms. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way.
Dimorphic fungi can define as a type of fungi which has a dual life cycle. The life cycle of a fungus is divided into two parts called anamorphic and teleomorphic stages. The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi.
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts moulds and mushrooms. They may be unicellular or filamentous. Edible and Poisonous Fungi Edible fungi Field mushrooms.
Mushrooms create what is called a mycelium network. Single-celled fungi are called yeast. In reality there are many sub-steps of the process.
We can understand the meaning of the term dimorphic just by breaking it into two in which Di. Some fungi are single-celled while others are multicellular. Fungi life cycle explained Wednesday March 2 2022 Edit.
Read about the life cycle of fungi in phylum Basidiomycota including karyogamy in Basidiomycota reproduction. Life cycle of fungi.
Fungi Life Cycle Introduction Life Cycle Faqs

Diagrammatic Representation Of Mushroom Life Cycle Download Scientific Diagram

Life Cycle Of An Am Fungus And The Different Steps During Am Development Download Scientific Diagram

Intro To The Fungi Life Cycle Plantsnap
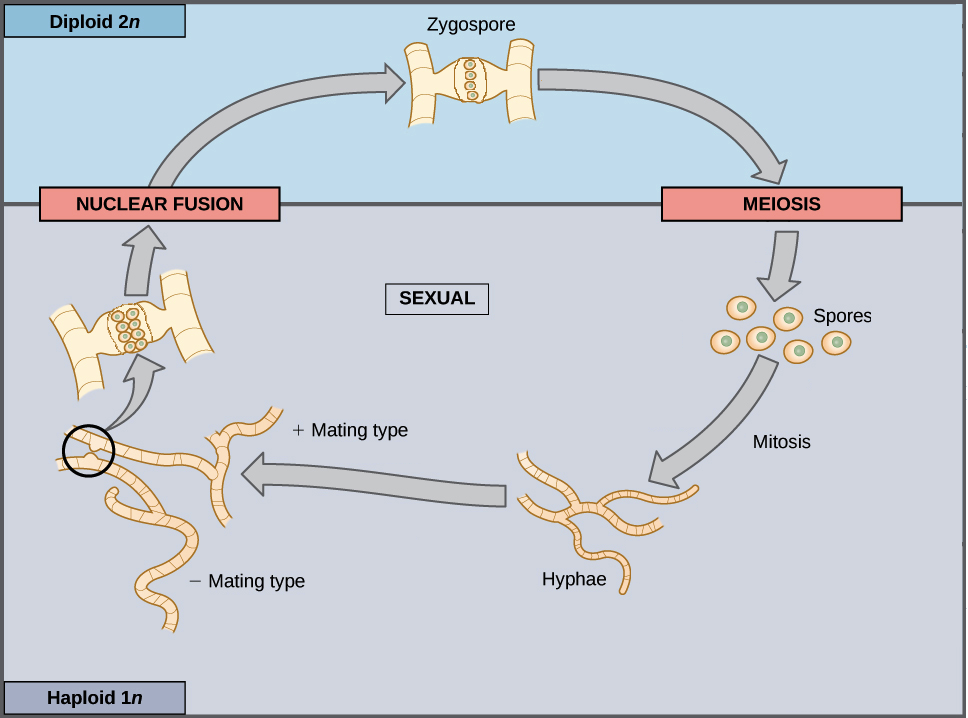
Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy

A Detailed Explanation Of The Mushroom Life Cycle Grocycle

Characteristics Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids
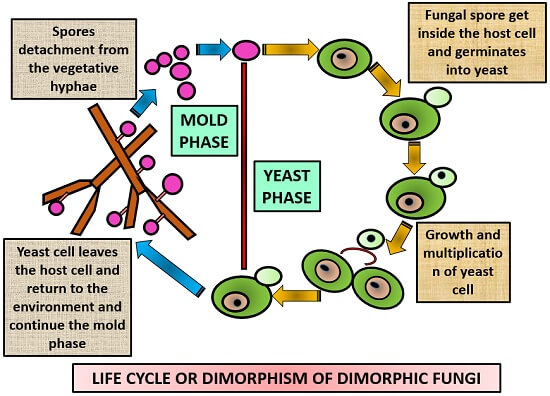
What Is Dimorphic Fungi Dimorphic Life Cycle Examples Transmission Biology Reader

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts

Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Reproduction In Fungi Life Cycle Of Fungi Youtube
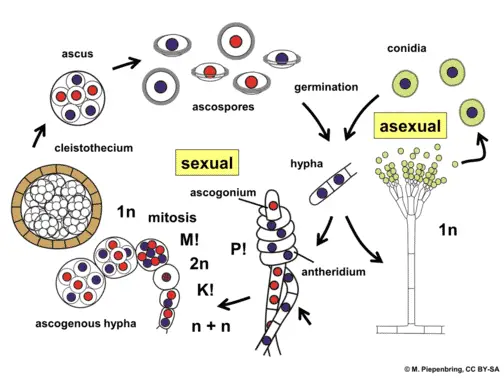
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity